
The company can make the notes payable journal entry by debiting the cash account and crediting the notes payable account on the date of receiving money after it signs the note agreement with its creditor. This journal entry is made to eliminate the notes payable that we have recorded at the time of issuance of the promissory note. Likewise, in this journal entry, both total assets and total liabilities on the balance sheet will decrease by the amount of payment. We can make the journal entry for the issuance of the promissory note to borrow the cash by debiting the cash account and crediting the notes payable account. Promissory note is a note that the issuer or retained earnings payer issues to a receiver for a promise to pay a certain amount of the money within a certain period of time. Likewise, we can make the journal entry for the issuance of promissory note by recording the promised amount into the notes payable account.
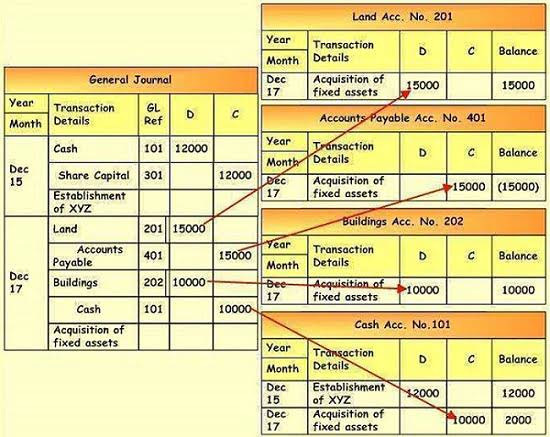
AP journal entry for assets purchase

The Wages Payable amount will be carried forward to the next accounting year. The Wages Expense amount will be zeroed out so that the next accounting year begins with a $0 balance. The balance in the liability account Accounts note payable journal entry Payable at the end of the year will carry forward to the next accounting year.
Accounts Payable Journal Entries
- Notice that the ending balance in the asset Supplies is now $725—the correct amount of supplies that the company actually has on hand.
- It comprises information related to the amount paid, applicable interest rate, name of the payer and payee, the maturity date, limitations if any, and the issuer’s signature with the date.
- For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
- Let’s assume that Sierra Sports was unableto make the payment due within 30 days.
It is crucial to accurately record notes payable to ensure that all financial liabilities are properly reflected on the balance sheet. Notes payables are written promissory notes to repay a specified amount to a lender on a predetermined date. These liabilities are recorded on the balance sheet and can be classified as either short-term or long-term, depending on their maturity. Notes payable differ from accounts payable in that they are formal agreements with specific terms, including the principal amount, interest rate, and maturity date. At the period-end, the company needs to recognize all accrued expenses that have incurred but not have been paid for yet. These accrued expenses include accrued interest on notes payable, in which the company needs to make journal entry by debiting interest expense account and crediting interest payable account.

Accounting for Interest Payable: Definition, Journal Entries, Example, and More
The systematic allocation of the cost of an asset from the balance sheet to Depreciation Expense on the income statement over the useful life of the asset. (The depreciation journal entry includes a debit to Depreciation Expense and a credit to Accumulated Depreciation, a contra asset account). The purpose is to allocate the cost to expense in order to comply with the matching principle.

Journal Entry for the Repayment of Bonds Payable
This should be the debit balance in Accounts Receivable minus the credit balance in Allowance for Doubtful Accounts. The credit balance in this account comes from the entry wherein Bad Debts Expense is debited. The amount in this entry may be a percentage of sales or it might be based on an aging analysis of the accounts receivables (also referred to as a percentage of receivables). The process of comparing the amounts in the Cash account in the general ledger to the amounts appearing on the bank statement.
- Whereas a subsequent liability arising will be recorded on the credit side.
- The amount in this entry may be a percentage of sales or it might be based on an aging analysis of the accounts receivables (also referred to as a percentage of receivables).
- Notes payable are often used for shorter-term financing needs, while bonds payable are suitable for raising large sums of capital over extended periods.
- (The depreciation journal entry includes a debit to Depreciation Expense and a credit to Accumulated Depreciation, a contra asset account).
- Revenues are deferred to a balance sheet liability account until they are earned in a later period.
- Essentially, any event that alters the amount your business owes to its suppliers requires an AP journal entry.
- Interest Payable is a liability account that reports the amount of interest the company owes as of the balance sheet date.
- For example, when a company borrows money, it increases its notes payable account and decreases its cash account.
- On this note, we promise to pay back the $1,000 amount with the interest of $50 on Jun 31 which is at the end of the second quarter of our accounting period.
Hence the income statement for December should report just one month of insurance cost of $400 ($2,400 divided by 6 months) in the account Insurance Expense. The balance sheet dated December 31 should report the cost of five months of the insurance coverage that has not yet been used up. To find notes payable in financial documents, look for the liability section on the balance sheet. Notes payables are typically listed under current liabilities or long-term liabilities, depending on the repayment schedule. The notes real estate cash flow payable account may be presented separately or combined with other liability accounts. The interest payable account is usually presented separately as a current liability.
Adjusting Entries – Asset Accounts
Likewise, the company needs to make the notes payable journal entry when it signs the promissory note to borrow money from the creditor. In this journal entry of issuing the $10,000 promissory note, both total assets and total liabilities on the balance sheet increase by the same amount of $10,000 as of July 1, 2021. Later, when we make the payment for the interest, we can make the journal entry to eliminate the interest payable we have recorded by debiting the interest payable account and crediting the cash account.
Understanding Notes Payable Journal Entries Explained
This note represents the principal amount of money that a lender lends to the borrower and on which the interest is to be accrued using the stated rate of interest. For example, on October 1, 2020, the company ABC Ltd. signs a $100,000, 10%, 6-month note that matures on March 31, 2021, to borrow the $100,000 money from the bank to meet its short-term financing needs. The company ABC receives the money on the signing date and as agreed in the note, it is required to back both principal and interest at the end of the note maturity. Accounts payable software automatically generates journal entries from invoices, reading and extracting relevant data such as invoice numbers, monetary amounts and supplier information.
